...
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
field_name | The field name to produce buckets from. Mandatory. |
value1,value2,value3... | They are the values of the field name you want to select counts fromcount. They have to be enclosed in square brackets. Optional. |
limit | Number of counts to show, i.e., number of buckets. Optional. |
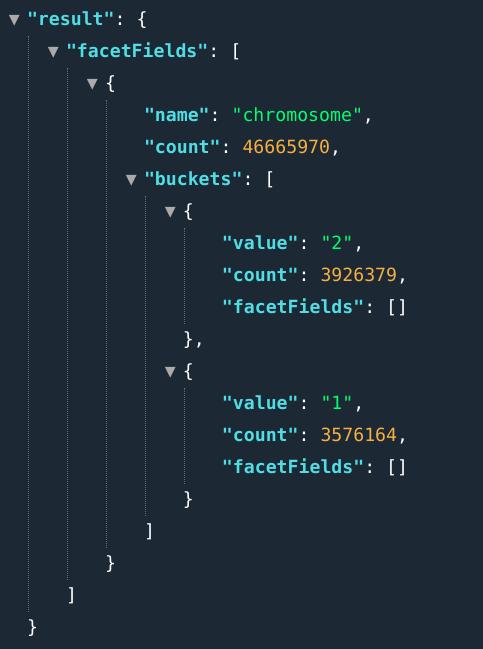
E.g.: ...&fields=chromosome[1,2]
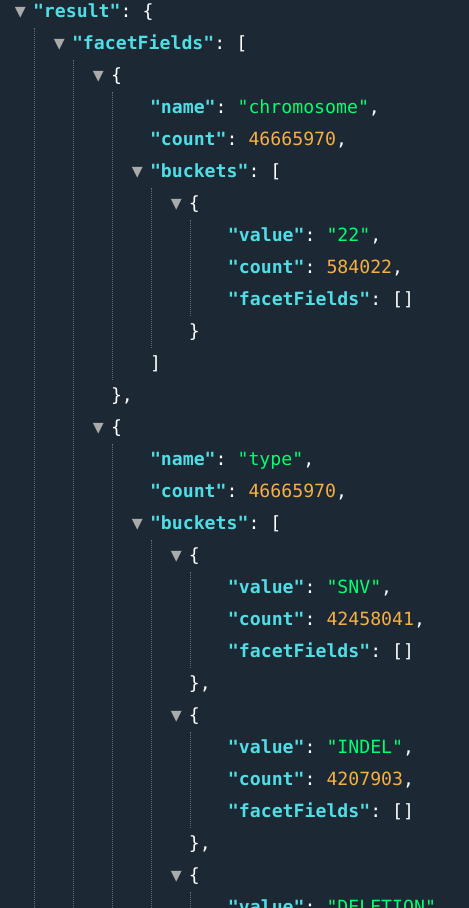
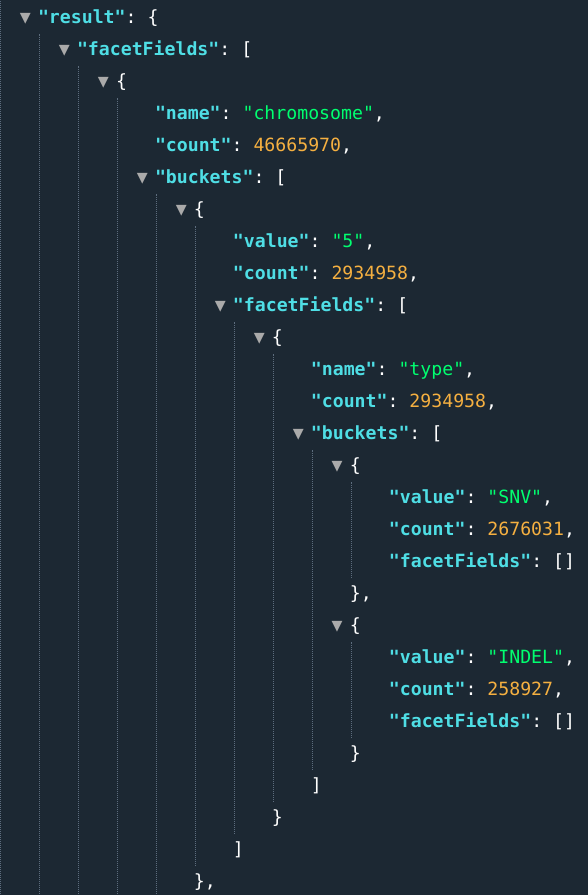
Users can query multiple stats by separating field names by semicolons.
E.g., .: ...&fields=chromosome[1,2];types
Ranges
When asking for ranges, the result contains multiple buckets over a numeric field. You must specify the field name, the lower and upper bounds and the step or bucket size.
...
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
field_name | The numeric field name to produce range buckets from. Mandatory |
start | Lower bound of the ranges. Mandatory. |
end | Upper bound of the ranges. Mandatory. |
step | Size of each range bucket produced. |
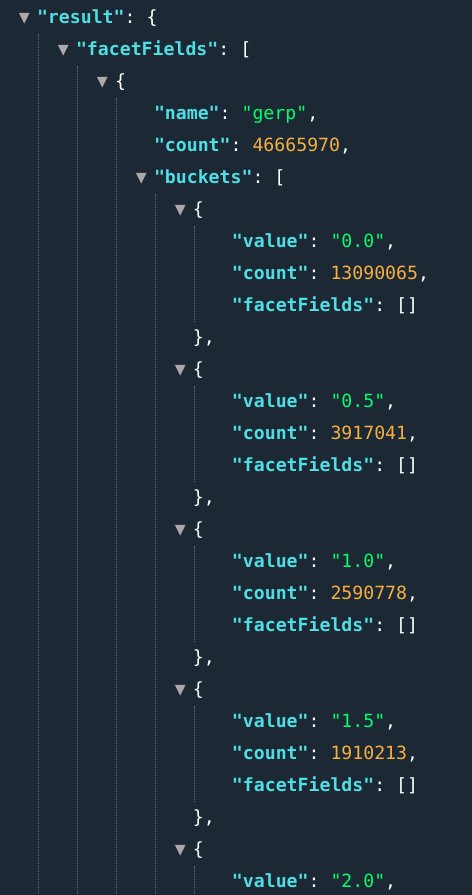
E.g.: ...&fields=gerp[0..10]:0.5
Aggregation functions
Aggregation functions, also called facet functions, analytic functions, or metrics, calculate something interesting over a domain (each facet bucket).
...
| Aggregation function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
avg | Average of numeric values | avg(gerp) |
min | Minimum value | min(sift) |
max | Maximum value | max(caddScaled) |
unique | Number of unique values | unique(biotypes) |
hll | Distributed cardinality estimate via hyper-log-log algorithm | hll(type) |
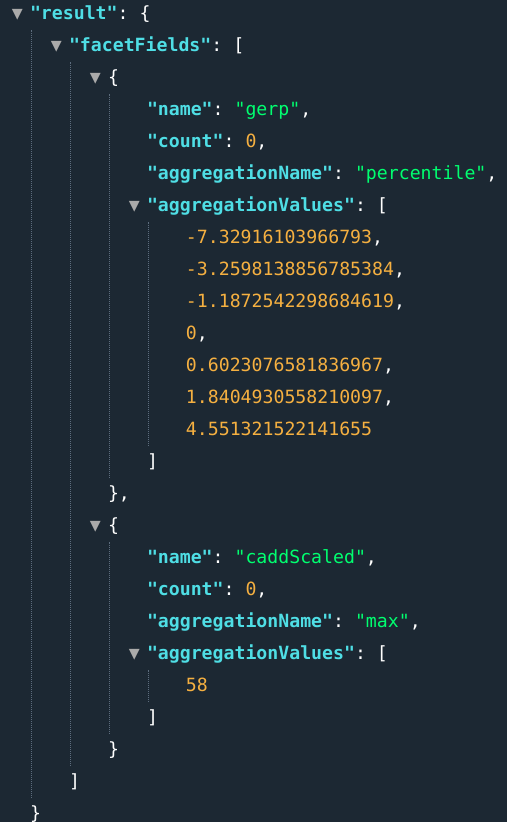
percentile | Percentile estimates via t-digest algorithm. Calculate the percentiles: 1, 10, 25, 50, 75, 90 and 99th. | percentile(gerp) |
sumsq | Sum of squares of field or function | sumsq(caddRaw) |
E.g., .: ...&fields=percentile(gerp);max(caddScaled)
Nested facets
Nested facets allow users to nest bucketing terms, ranges or aggregations. In order to specify nested facets you must use the symbols >>
E.g., .: ...&fields=chromosome[5,6]>>type