Versions Compared
Key
- This line was added.
- This line was removed.
- Formatting was changed.
Overview
We believe that it is important to keep the databases mostly unaware in which format the data was originally stored. A reference to this format will only be stored for specific purposes involving file transfers.
Data model for variants and alignments have been designed and implemented in Java. They explicitly specify the most commonly used fields, and at the same time provide mechanisms for preserving all the information of a certain format. For instance, the fields specified for a variant would be (among others) chromosome, position, reference and alternatives; if a VCF file is being stored, then columns such as INFO are also saved in a key-value data structure.
OpenCGA imports different data models from OpenCB Biodata and GA4GH such as Variant and Alignment data models; while others such as Catalog Data Models have been developed in OpenCGA itself. In next sections you will find
Catalog
Catalog models all the information about users, projects, studies, files, jobs, samples and clinical data among others. This has been developed internally in OpenCGA Catalog component, you can find a more detailed information at Catalog > Catalog Data Models.
Storage
Variant
OpenCGA Variant data model has been developed in OpenCB Biodata and is used in different OpenCB projects such as CellBase or Oskar.
Alignment
OpenCGA takes Alignment data model specification from GA4GH and the implementation from OpenCB GA4GH. See a full description at Alignment Data Model.OpenCGA Alignment Engine provides a solution to storage and process sequence alignment data from Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) projects. The Alignment Engine supports the most common alignment file formats, i.e.: SAM, BAM and CRAM, and takes the alignment data model specification from GA4GH and the implementation from OpenCB GA4GH. See a full description at Alignment Data Model.
We do not define or endorse any dedicated unaligned sequence data format. Instead we recommend storing such data in one of the alignment formats (SAM, BAM, or CRAM) with the unmapped flag set.
OpenCGA alignment engine provides the following analysis:
- Index analysis
To index a coordinate-sorted alignment file (BAM or CRAM) for fast random access. This index is needed when region parameters are used to limit the query analysis to particular regions of interest.
- Query analysis
This analysis outputs those alignments matching the specified filters, such as minimum mapping quality, maximum insert size, maximum number of mismatches in the alignment, properly paired alignments,... In addition, users may specify one or more comma-separated regions to restrict output to only those alignments which overlap the specified region(s). Note that use of region specifications requires a coordinate-sorted and indexed input file (in BAM or CRAM format).
- Coverage analysis
This analysis takes a coordinate-sorted and indexed alignment file (in BAM or CRAM format) as input and generates a coverage file (in BigWig format). The coverage is calculated as the number of reads per window of a user-defined size, if window size is equal to 1, the coverage is the number of reads per position. Once coverage is computed, the read coverage over multiple genomic regions can be fetched quite quickly.
- Statistics analysis
OpenCGA computes statistics for a given alignment file by using the samtools stats command. Alignment statistics are indexed in order to allow users to query for alignment files according to those statistics.
In addtion, OpenCGA provides wrappers to the following third-party alignment software packages:
- FastQC: a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data.
- BWA: a software package for mapping low-divergent sequences against a large reference genome.
- Samtools: a program for interacting with high-throughput sequencing data in SAM, BAM and CRAM formats.
- deepTools: a suite of python tools particularly developed for the efficient analysis of high-throughput sequencing data, such as ChIP-seq, RNA-seq or MNase-seq.
OpenCGA Alignment User Interfaces
OpenCGA provides two interfaces to allow users execute the alignment tools and analysis:
- Command line inteface
- RESTful web services interface
OpenCGA command line interface
The OpenCGA command line interface to manage alignment data is accessible through the script opencga.sh using the command alignments:
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
$ ./opencga.sh alignments
Usage: opencga.sh alignments <subcommand> [options]
Subcommands:
index Index alignment file
query Search over indexed alignments
stats-run Compute stats for a given alignment file
stats-info Retrieve stats for a given alignment file
stats-query Fetch alignment files according to their stats
coverage-run Compute coverage for a given alignemnt file
coverage-query Query the coverage of an alignment file for regions or genes
coverage-ratio Compute coverage ratio from file #1 vs file #2, (e.g. somatic vs germline)
bwa BWA is a software package for mapping low-divergent sequences against a large reference genome.
samtools Samtools is a program for interacting with high-throughput sequencing data in SAM, BAM and CRAM formats.
deeptools Deeptools is a suite of python tools particularly developed for the efficient analysis of high-throughput sequencing data, such as ChIP-seq, RNA-seq or MNase-seq.
fastqc A quality control tool for high throughput sequence data.
|
The tutorial Working with Alignment Data shows how to use the OpenCGA alignment commandline.
OpenCGA RESTful web services interface
Next image shows the OpenCGA RESTfull web services to manage alignment data:
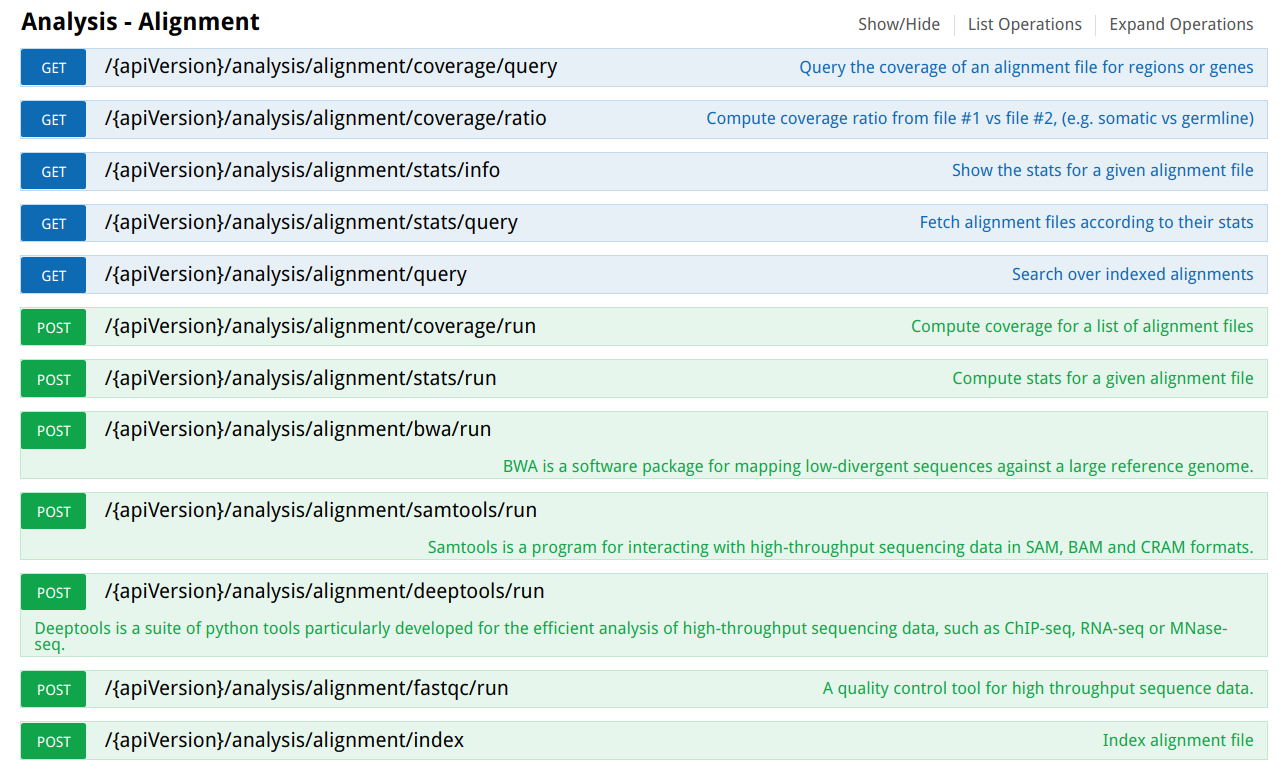 Image Added
Image Added
Table of Contents:
| Table of Contents | ||
|---|---|---|
|